Monday, December 27, 2010
Saturday, December 11, 2010
Friday, December 10, 2010
Friday, December 3, 2010
Object Oriented Design(s) in R
Check out this SlideShare Presentation:
Object Oriented Design(s) in R
View more presentations from Romain Francois.
Thursday, December 2, 2010
Monday, November 29, 2010
Tuesday, November 23, 2010
NYC Semantic Web Meetup, Nov 2010
Check out this SlideShare Presentation:
NYC Semantic Web Meetup, Nov 2010
View more presentations from Jay Myers.
Monday, November 22, 2010
Saturday, November 13, 2010
Friday, November 12, 2010
The Making of Pie
Check out this SlideShare Presentation:
The Making of Pie
View more presentations from Sarah Allen.
Rc2010 refinements
Check out this SlideShare Presentation:
Rc2010 refinements
View more presentations from Shugo Maeda.
LinkedIn OAuth: Zero To Hero
Check out this SlideShare Presentation:
LinkedIn OAuth: Zero To Hero
View more presentations from Taylor Singletary.
Thursday, November 11, 2010
Tuesday, November 9, 2010
Writing HTML5 apps with Google App Engine, Google Closure Library and Clojure
Check out this SlideShare Presentation:
Monday, November 8, 2010
Wednesday, November 3, 2010
Tuesday, November 2, 2010
Monday, November 1, 2010
Tuesday, October 26, 2010
Monday, October 25, 2010
Friday, October 22, 2010
Thursday, October 21, 2010
Tuesday, October 19, 2010
Friday, October 15, 2010
Tuesday, October 12, 2010
Sunday, October 10, 2010
Friday, October 8, 2010
Articles 10-08-2010
Revving Up Your Hibernate Engine
Introducing Templates for jQuery
Android Text-To-Speech Application
RESTful Web services and signatures
Concurrency Revolution From a Hardware Perspective
Amr Elssamadisy: Why Agile Works
Sociology and Scrum
Bob Galen Talks Scrum
Multi-machine EC2 Cassandra Setup in 30 minutes
Introducing Templates for jQuery
Android Text-To-Speech Application
RESTful Web services and signatures
Concurrency Revolution From a Hardware Perspective
Amr Elssamadisy: Why Agile Works
Sociology and Scrum
Bob Galen Talks Scrum
Multi-machine EC2 Cassandra Setup in 30 minutes
Thursday, October 7, 2010
Tuesday, October 5, 2010
Monday, October 4, 2010
36 places where to submit your startup for some coverage
Source
1. Killer Startups
2. Springwise
3. CrunchBase
4. GotoWeb2.0
5. StartupMeme
6. SimpleSpark
7. VentureBeat Profiles
8. FeedMyApp
9. BigStartups
10. GreatWebApps
11. Wwwhatsnew
12. 101 Best Websites
13. MakeUseOf
14. LaunchFeed
15. MoMB
16. Demo Girl
17. WebDev 2.0
18. DzineBlog
19. Sociable Blog
20. Emily Chang
21. Rev2
22. Ziipa
23. On The App
24. Next Web App
25. DIY Startup News
26. AppUseful
27. Startup Booster
28. Paggu
29. Robin Speziale
30. Submit Startup
31. TechHotSpot
32. YouNoodle
33. Lovely Pages
34. Generation-y Startup
35. TechPluto
36. Netted
1. Killer Startups
2. Springwise
3. CrunchBase
4. GotoWeb2.0
5. StartupMeme
6. SimpleSpark
7. VentureBeat Profiles
8. FeedMyApp
9. BigStartups
10. GreatWebApps
11. Wwwhatsnew
12. 101 Best Websites
13. MakeUseOf
14. LaunchFeed
15. MoMB
16. Demo Girl
17. WebDev 2.0
18. DzineBlog
19. Sociable Blog
20. Emily Chang
21. Rev2
22. Ziipa
23. On The App
24. Next Web App
25. DIY Startup News
26. AppUseful
27. Startup Booster
28. Paggu
29. Robin Speziale
30. Submit Startup
31. TechHotSpot
32. YouNoodle
33. Lovely Pages
34. Generation-y Startup
35. TechPluto
36. Netted
Thursday, September 30, 2010
Wednesday, September 29, 2010
Solaris Express, Developer Edition
Solaris Express, Developer Edition 2/07
Introduction to the Solaris Development Environment
[Download this Book]Solaris Express, Developer Edition Installation Guide
[Download this Book]Solaris Express, Developer Edition Release Notes
[Download this Book]Solaris Express, Developer Edition What's New
[Download this Book]
Solaris Express Software Developer Collection
Device Driver Tutorial [Download this Book] Linker and Libraries Guide [Download this Book] SIP API Developer's Guide [Download this Book] Solaris Containers: Resource Management and
Solaris Zones Developer's Guide
[Download this Book]Solaris Dynamic Tracing Guide
[Download this Book]Solaris Security for Developers Guide
[Download this Book]-
Writing Device Drivers [Download this Book]
Solaris Express System Administrator Collection
-
Solaris Tunable Parameters Reference Manual
[Download this Book] Solaris Volume Manager Administration Guide
[Download this Book]Solaris ZFS Administration Guide
[Download this Book]System Administration Guide: Advanced Administration
[Download this Book]System Administration Guide: Basic Administration
[Download this Book]System Administration Guide: Devices and File Systems
[Download this Book]System Administration Guide: IP Services
[Download this Book]Naming and Directory Services (DNS, NIS, and LDAP)
[Download this Book]System Administration Guide: Network Services
[Download this Book]System Administration Guide: Security Services
[Download this Book]Solaris Containers-Resource Management and Solaris Zones
[Download this Book]
Solaris Express Reference Manual Collection
man pages section 1: User Commands
[Download this Book]man pages section 1M: System Administration Commands
[Download this Book]man pages section 2: System Calls
[Download this Book]man pages section 3: Basic Library Functions
[Download this Book]man pages section 3: Curses Library Functions
[Download this Book]man pages section 3: Extended Library Functions
[Download this Book]man pages section 3: Library Interfaces and Headers
[Download this Book]-
man pages section 3: Multimedia Library Functions man pages section 3: Networking Library Functions
[Download this Book]man pages section 3: Realtime Library Functions
[Download this Book]man pages section 4: File Formats
[Download this Book]man pages section 5: Standards, Environments, and Macros
[Download this Book]man pages section 7: Device and Network Interfaces
[Download this Book]man pages section 9: DDI and DKI Driver Entry Points
[Download this Book]man pages section 9: DDI and DKI Kernel Functions
[Download this Book]man pages section 9: DDI and DKI Properties and Data Structures
[Download this Book]
Solaris Trusted Extensions Collection
Compartmented Mode Workstation Labeling: Encodings Format
[Download this Book]Solaris Trusted Extensions Administrator's Procedures
[Download this Book]Solaris Trusted Extensions Developer's Guide
[Download this Book]Solaris Trusted Extensions Installation and Configuration
[Download this Book]Solaris Trusted Extensions Label Administration
[Download this Book]Solaris Trusted Extensions Reference Manual
[Download this Book]Solaris Trusted Extensions Transition Guide
[Download this Book]Solaris Trusted Extensions User's Guide
[Download this Book]
Solaris Express Release and Installation Collection
Solaris Live Upgrade and Upgrade Planning
[Download this Book]Basic Installations
[Download this Book]Custom JumpStart and Advanced Installations
[Download this Book]Network-Based Installations
[Download this Book]Planning for Installation and Upgrade
[Download this Book]-
Solaris Flash Archives (Creation and Installation) Solaris Express Package List
[Download this Book]Solaris Express Release Notes
[Download this Book]Solaris Express, Developer Edition What's New
[Download this Book]
Monday, September 13, 2010
Habits Of Mind - Math
This is still a work in progress (and feedback would be greatly appreciated), but I've decided to explicitly teach (and assess...more on that later) 4 "categories" of mathematics this year.
- Skills (I know how to...)
- Concepts (I understand and can explain why...)
- Connections (I see and can explain the relationship between...)
- Mathematical Habits of Mind (I can use and appreciate the process of...)
Friday, September 3, 2010
Google interview questions
Here's a list of 140 Google interview questions. Many of our clients have interviewed and received Google job offers.
continue...
continue...
Tuesday, January 12, 2010
Thursday, January 7, 2010
How the CPU Executes Program Instructions
How Computers Work: The CPU and Memory
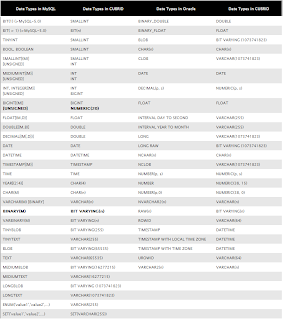
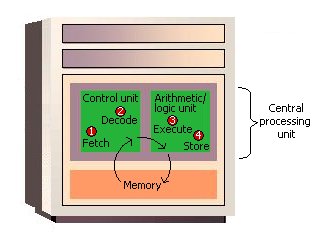 |
| Figure 2: The Machine Cycle |
Before an instruction can be executed, program instructions and data must be placed into memory from an input device or a secondary storage device (the process is further complicated by the fact that, as we noted earlier, the data will probably make a temporary stop in a register). As Figure 2 shows, once the necessary data and instruction are in memory, the central processing unit performs the following four steps for each instruction:
- The control unit fetches (gets) the instruction from memory.
- The control unit decodes the instruction (decides what it means) and directs that the necessary data be moved from memory to the arithmetic/logic unit. These first two steps together are called instruction time, or I-time.
- The arithmetic/logic unit executes the arithmetic or logical instruction. That is, the ALU is given control and performs the actual operation on the data.
- Thc arithmetic/logic unit stores the result of this operation in memory or in a register. Steps 3 and 4 together are called execution time, or E-time.
The control unit eventually directs memory to release the result to an output device or a secondary storage device. The combination of I-time and E-time is called the machine cycle. Figure 3 shows an instruction going through the machine cycle.
Each central processing unit has an internal clock that produces pulses at a fixed rate to synchronize all computer operations. A single machine-cycle instruction may be made up of a substantial number of sub-instructions, each of which must take at least one clock cycle. Each type of central processing unit is designed to understand a specific group of instructions called the instruction set. Just as there are many different languages that people understand, so each different type of CPU has an instruction set it understands. Therefore, one CPU-such as the one for a Compaq personal computer-cannot understand the instruction set from another CPU-say, for a Macintosh.
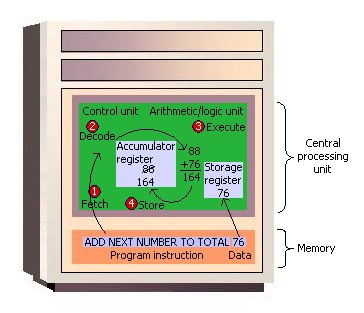 |
| Figure 3: The Machine Cycle in Action |
It is one thing to have instructions and data somewhere in memory and quite another for the control unit to be able to find them. How does it do this?
 |
| Figure 4: Memory Addresses Like Mailboxes |
Figure 4 shows how a program manipulates data in memory. A payroll program, for example, may give instructions to put the rate of pay in location 3 and the number of hours worked in location 6. To compute the employee's salary, then, instructions tell the computer to multiply the data in location 3 by the data in location 6 and move the result to location 8. The choice of locations is arbitrary - any locations that are not already spoken for can be used. Programmers using programming languages, however, do not have to worry about the actual address numbers, because each data address is referred to by a name. The name is called a symbolic address. In this example, the symbolic address names are Rate, Hours, and Salary.
Wednesday, January 6, 2010
Linux Commands
Linux Commands I Hardly Knew
Ubuntu
How To Enable Vi Syntax Highlighting In Ubuntu
sudo apt-get remove vim-tiny
sudo apt-get install vim
sudo vi /etc/vim/vimrc
( Remove the quote mark from the "syntax on" line, uncommenting it)
Adding Environment variables...
$ echo 'export GOROOT=$HOME/go' >> ~/.bashrc
$ echo 'export GOOS=linux' >> ~/.bashrc
$ echo 'export GOARCH=386' >> ~/.bashrc
$ echo 'export GOBIN=$GOROOT/bin' >> ~/.bashrc
$ echo 'export PATH=$PATH:$GOBIN' >> ~/.bashrc
$ . ~/.bashrc
You can source the files instead of restarting the machine:source /etc/profile
source ~/.bashrc
ALLOWING OTHER USERS TO RUN SUDO
By default, only the user who installed the system is permitted to run sudo. To add more administrators, i. e. users who can run sudo, you have to add these users to the group 'admin' by doing one of the following steps:
sudo adduser username admin
To enable the root account (i.e. set a password) use:
sudo passwd root
Afterwards, edit /etc/sudoers and comment out the line
%admin ALL=(ALL) ALL
to disable sudo access to members of the admin group.
Tuesday, January 5, 2010
Towards a Standard Parser Generator
Abstract
Developing parsers for "little" languages is a common task for many software developers. People have frequently requested inclusion of a specific parser generator framework into the Python library. In this paper, we compare several Python parser generators, using the XPath language as an application. Criteria for comparison are ease of use, performance, and ease of deployment. Using these criteria, we give a recommendation for including parser generators into the standard library.. Keywords: Parsers, XPath, YAPPS, Spark, BisonGen
Algorithm Education in Python
Abstract
Design and analysis of algorithms are a fundamental topic in computer science and engineering education. Many algorithms courses include programming assignments to help students better understand the algorithms. Unfortunately, the use of traditional programming languages forces students to deal with details of data structures and supporting routines, rather than algorithm design. Python represents an algorithm-oriented language that has been sorely needed in education. The advantages of Python include its textbook-like syntax and interactivity that encourages experimentation. More importantly, we report our novel use of Python for representing aggregate data structures such as graphs and flow networks in a concise textual form, which not only encourages students to experiment with the algorithms but also dramatically cuts development time. These features have been implemented in a graduate level algorithms course with successful results.
continue...
Design and analysis of algorithms are a fundamental topic in computer science and engineering education. Many algorithms courses include programming assignments to help students better understand the algorithms. Unfortunately, the use of traditional programming languages forces students to deal with details of data structures and supporting routines, rather than algorithm design. Python represents an algorithm-oriented language that has been sorely needed in education. The advantages of Python include its textbook-like syntax and interactivity that encourages experimentation. More importantly, we report our novel use of Python for representing aggregate data structures such as graphs and flow networks in a concise textual form, which not only encourages students to experiment with the algorithms but also dramatically cuts development time. These features have been implemented in a graduate level algorithms course with successful results.
continue...
Saturday, January 2, 2010
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)